Definition Of Penetration Bitumen
The penetration grades bitumen is refinery bitumen which is produced by different viscosity. In fact, Penetration bitumen is semi hard black material known as petroleum grade bitumen. The penetration test is carried out to characterize the bitumen, based on the hardness. Therefore, it has the name penetration bitumen.Penetration Grade Bitumen is a standard bitumen usually used as a Paving Grade Bitumen essential for road construction and for the production of asphalt pavements with superior properties, and it’s very important once it bounds the aggregates and creates a unique cohesion and stability to the bituminous mix.

Actually it is Bitumen classified using the penetration property. Penetration grading’s basic assumption is that the less viscous the asphalt, the deeper the needle will penetrate. Bitumen which is produced during the process of oxidation of vacuum bottom (the Bitumen production feedstock that derives from distillation tower residue in vacuum oil refineries) at bitumen production unit in a manner that its penetration point (kind of test to indicate the hardness of bitumen) in specified group is classified in different grade of it.
This grade of Bitumen is mainly used in the manufacture of hot mix asphalt for bases and wearing courses.
The penetration of bituminous material is its consistency expressed as the distance in tenths of a millimeter that a standard needle penetrates vertically into a specimen of the material under specified conditions of temperature, load and duration of loading. Grades of straight-run bitumen are designated by two penetration values, for example, 40/50, 60/80, 80/100 etc.; the Penetration of an actual sample of the bitumen in any grade should fall between the lower and upper value given.
Penetration Grade bitumens are specified by the penetration and softening point test. Designation is by penetration range only. The penetration grade bitumens have a thermoplastic property which causes the material to soften at high temperatures and to harden at lower temperatures. This unique temperature/viscosity relationship is important when determining the performance parameters such as the adhesion, rheology, durability and application temperatures of bitumen.
Sources of Bitumen
Bitumen is generally obtained from the following three sources:
- Naturally occurring
- Extracted from Limestone and Sandstone
- From Oil Refineries
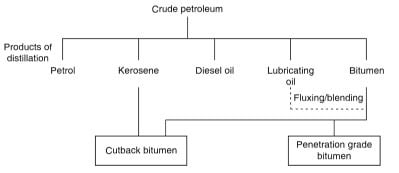
The manufacture of bitumen is a lengthy process which is represented briefly in the below flowchart. The bitumen is a residual material. The final bitumen property will depend upon the extent of extraction, the viscosity, and the distillation process.
The present refinery plant has the capability to extract bitumen more precisely as the required viscosity and consistency.
Penetration Grading
Advantages
- Consistency at average service temperature
- Short testing time
- Adaptable to field applications (contamination)
- Relatively low equipment cost
Disadvantages
- Grade overlap (85-100 grade = AC-5, AC-10, or AC-20)
- Similitude at 77 °F deceptive to
- performance at higher and lower service temperatures
- Rates of test (shear rate) high and variable
- No viscosity available near mixing and compaction temperatures
In different regions and countries, different Standards and Grading systems are used for determining the quality of petroleum bituminous Binders. The most recognized standards for petroleum bitumen are published by
- European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
- Deutsche Industrie Norm (DIN EN)
- Association Française de Normalisation (AFNOR – NF EN)
- BSI Standards – the UK’s National Standards Body (NSB – BS EN)
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM)
- American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO)
- South African Standard Organization (SABS)
- Standards Australia (AS)
Penetration grades are listed as a range of penetration units (one penetration unit = 0.1 mm) such as 120 – 150. Penetration grades specified in AASHTO M 20 and ASTM D 946 are listed in below table
| Penetration Grade | Comments |
|---|---|
| 40 – 50 | Hardest grade. |
| 60 – 70 | Typical grades used in the U.S. |
| 85 – 100 | |
| 120 – 150 | |
| 200 – 300 | Softest grade. Used for cold climates such as northern Canada |
Penetration Grade Bitumen Specification (AASHTO M 20 and ASTM D 946)
| Units | 40/50 | 60/70 | 80/100 | 100/120 | Test Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity @25°C | – | 1.01-1.06 | 1.01-1.06 | 1.01-1.05 | 1.01-1.04 | ASTM D-70 |
| Penetration @25°C, 100gm, 5sec | 0.1MM | 40-50 | 60-70 | 80-100 | 100-120 | ASTM D-5 |
| Softening Point, Ring & Ball | °C | 52-60 | 49-56 | 45-52 | 42-49 | ASTM D-36 |
| Ductility @25°C, after TFOT, Min | CM | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ASTM D-113 |
| Loss on Heating, Max | %Wt | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ASTM D-6 |
| Drop in Penetration after Heating, Max | % | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | ASTM D-6 & D-5 |
| Flash Point Cleveland open cup, Min | °C | 250.0 | 250.0 | 232.0 | 250.0 | ASTM D-92 |
| Solubility in CS2, Min | %Wt | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.5 | ASTM D-4 |
| Organic Matter Insoluble in CS2, Max | %Wt | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | ASTM D-4 |
| Sport Test | – | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | *A.A.S.H.O.T.102 |
Bitumen Specification European Standard (BS EN 12591)
| Units | 35-50 | 40-60 | 50-70 | 70-100 | 100-150 | Test Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration @25°C, 100gm, 5sec | 0.1MM | 35-50 | 40-60 | 50-70 | 70-100 | 100-150 | EN 1426 |
| Softening Point, Ring & Ball | °C | 50-58 | 48-56 | 46-54 | 43-51 | 39-47 | EN 1427 |
| Resistace to Hardening@163°C | |||||||
| – Change in mass, Max | %Wt | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 | EN 12607-1 |
| – Retained Penetration, Min | 0.1MM | 53 | 50 | 50 | 46 | 43 | |
| – Softening point after hardinging, Min | °C | 52 | 49 | 48 | 45 | 41 | |
| Other Properties | |||||||
| Flash Point Cleveland open cup, Min | °C | 240 | 230 | 230 | 230 | 230 | EN ISO 2592 |
| Solubility in CS2, Min | %Wt | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.0 | EN 12592 |
| Kinematic Viscocity @135°C, Min | mm2/S | 370 | 325 | 295 | 230 | 175 | EN 12595 |
-
ASTM D946-09
-
EN 12591-2009








