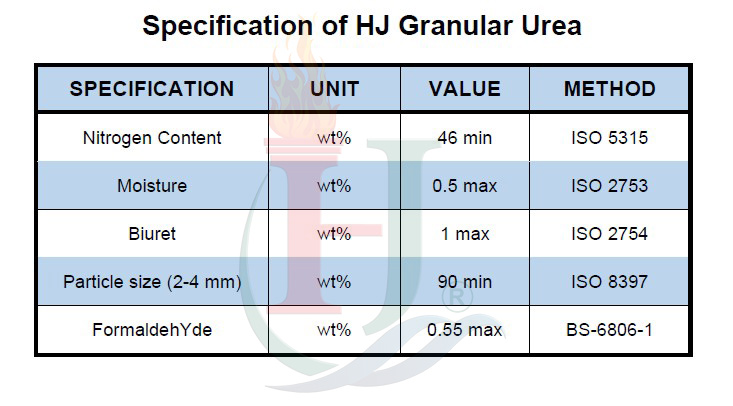
Description of Urea
Urea is a raw material used in the manufacture of many chemicals, such as various plastics, urea-formaldehyde resins, and adhesives. It is also essential for making feedstock, glue, fertilizer, commercial products, and resin production.
Urea also is known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two –NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group.
It is highly soluble in water and has a pKa close to zero. Urea is essentially the waste produced when the body metabolizes protein. It is not only produced by humans, but also by many other mammals, as well as amphibians and some fish. Urea was the first natural compound to be artificially synthesized using inorganic compounds — a scientific breakthrough.

The primary raw material used to manufacture urea is natural gas, which ties the costs directly to gas prices. Consequently, new plants are only being built in areas with large natural gas reserves where prices are lower. The finished product is transported around the globe in large shipments of 30,000 metric tons. The market price for urea is directly related to the world price of natural gas and the demand for agricultural products. Prices can be very volatile, and at times, unpredictable.
Application of Urea
1.Agriculture
2.Chemical industry
3.Explosives
4.Automobile systems
5.Laboratory uses
6.Medical use
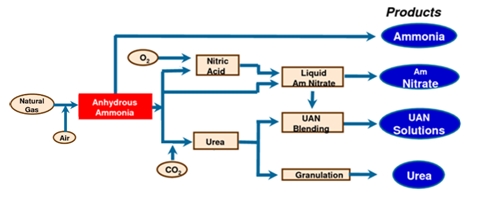
Manufacturing Process Of Urea